
2021 in history was considered an important year for the major changes Google brought in its algorithm that completely changed the game. It improved user experience to a great expanse.
1. Page Experience Updates For Desktop
The update was announced on November 4, 2021, but rolled out in 2022 on February 22 and ended on 3 March.
First, we are all familiar with mobile-friendly page experience, now page experience for desktops is quite similar to all the parameters except that of mobile-friendliness.
That means that your desktop screen is measured in the same way as your mobile screen experience.
Largest contentful paint (LPC): Scale for the measurement of perceived load speed and landmarks when the page’s main content has loaded.
Cumulative layout shift (CLS): measures visual stability and layout shift that affects user experience.
First input delay (FID): the response time that the user first took to interact with the page.
HTTPS security: a protocol that protects data shared by users with the site page.
Absence of intrusive interstitials: the popups on the page screen distract users from viewing the actual content.
The update made core web vitals a desktop ranking factor. Above are some of the factors that affect desktop ranking.
Before this update Google Search Console report allowed sites to review their desktop core web vitals.
(what is a Google search console is a free service offered by Google that helps you monitor and troubleshoot your website performance on search engines)
2. Product Review Update:
December product review update
Rolled out on 1 December and lasted till 21 December
Like any other product review updates were aimed at rewarding high-quality honest reviews rather than overloaded with marketing and selling perspective reviews or rather less informative reviews. Because Google believes that karma is the guy on the screen and also on the rankings in SERPs
The volatility was highly affected by this update. This update was quite long and took around three weeks to roll out.
With this update, there were two extra guidelines Google added to its PRU rulebook
- To add evidence of personal experience with the product and services
- To provide links to multiple sellers from which users can directly buy the product or services if convinced.
This guideline unfortunately or fortunately was not implicated directly as sites did not add links and proofs did not lose their rankings. As the guidelines were Google is planning the landing of these better quality product reviews and not where how currently algorithms perform.
April product review update.
Here is the change of volatility in SERPs during the update.
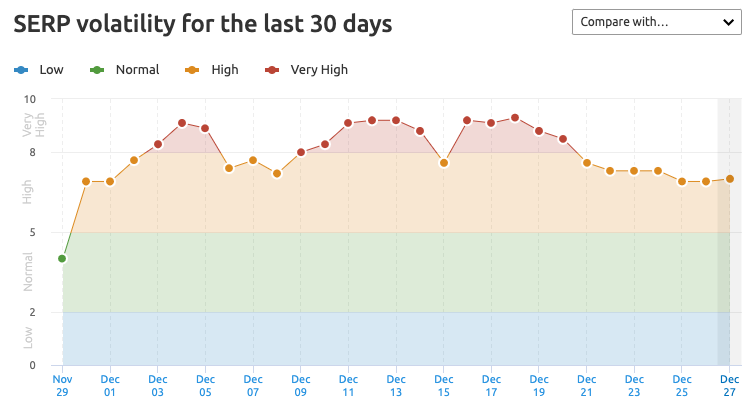
April product review update:
The first-ever product review was released in April of 2021 on 8 it was completed by 22.
The idea behind this was to reward expert reviews rather than just content that describes a bunch of products. With this google educated webmasters and experts and how it was going to work, with its guidelines.
What should be included in the product review according to the guidelines of the google?
- To provide users with knowledgeable analysis and research of the product
- To upload authentic content written by field experts and enthusiasts
- To provide competitor analysis of the product
- To provide with Pros and Cons of the product
- To inform about key decision-making factors
- To provide the new features and how the product has evolved
3. Core Update:
What are core updates?
Google uses core updates as a means of rewarding websites that ethically obey their spam and algorithm but still don’t rank well on search engine results pages.
However, the updates do not expressly target harm to pages and websites that violate the guidelines.
The primary update’s modifications include a review of the material as a whole and a ranking of the less-rewarded websites.
Why does Google release so many core updates?
to provide credit to pages that have not been ranked even if they offer excellent added value, a wealth of experience, and user-friendly content.
to stop duplicate and non-authoritative information from appearing in search engine results.
to put an end to those who try to undermine Google’s goal of giving its users the most relevant information possible. via questionable SEO techniques.
Core improvements aim to bring to the fore credibility, know-how, and authenticity that Google and its users can rely on.
Core update November:
The update hit the health industry the most; all other industries were affected all over, and the volatility spiked to a peak. For the initial two days, the volatility stayed at its peak, and then again normalcy was declared, like always.
Desktop SERPs peaked by 12% volatility
Mobile SERPs peaked by 23% volatility
Average volatility peaked at 20% in comparison to the July core update.
Google Algorithm Update History [+ Latest SEO Changes]
July core update:
Was announced on 2 June, started to roll out on July 1st, and ended on 12 July.
This core update was to be part of the June core update, but as it was the first ever Google introduced the core update. They left a part of it for the June update for July.
The core update brought changes that were hardly noticeable by most sites and pages.
June core update:
The first-ever core update of the year was released on 2 June and ended on 12 June.
Google had high expectations with the core update but they could not implement all the updates planned and thus the second part of this update was left out for July
Google had admitted “Some of our planned improvements for the June 2021 update aren’t quite ready, so we’re moving ahead with the parts that are, then we will follow with the rest with the July 2021 update. Most sites won’t notice either of these updates, as is typical with any core updates.”
Many sites saw a spike in their SERP volatility, while many had negative impacts.
It was advised to perform a site audit and correct what was wrong before the site got hit by the other core update of July.
4. Spam Update:
What is a Spam Update?
Google quoted “Google’s automated systems to detect search spam are constantly running, we occasionally make notable improvements to how they work. When we do, we refer to this as a spam update and share when they happen on our list of Google Search ranking updates.”
Spam update of November:
Was released on 3 November 2021 and completed on 11 November.
With this update, Google had advised websites to focus on SEO best practices. The update focused on improving Google’s ability to update its spam detection techniques.
There had already been three previous spam updates which makes searches spam-free.
In the previous year, google had blocked 25 billion spammy pages from being indexed by search engine algorithms.
Websites that follow the webmaster guidelines ethically and do not mess with Google algorithms and deceive it for the sake of ranking do not need to fear Google spam updates.
June spam update (part 1)
Started on June 23 the update was completed within 24 hours
Same as any other spam update, this Google spam update was focused on fighting web spam. Multiple spam updates occur many times a year which indicates that Google wants the web to be completely safe for its users and top every black hat SEO practices, which is unsafe for its users.
June spam update (part 2)
Started on June 28 and just like the previous update was completed within 24 hours.
Part two of the previous spam update rolled out after 8 days, while the purpose remained the same for both updates. The second update was a step closer to enhancing the spam detenting Google algorithm
5. Link Spam Update
Link spam update rolled out on 26 July 2021
Was focused on nullifying spam links on websites across many languages.
The update targeted guests, sponsored and affiliate content
Google has guidelines for using each of these links:
Affiliate: google asks sites participating in affiliate programs to qualify links with
rel-” sponsored”. Irrespective of links being created manually dynamically.
Links sponsored posts: links that are paid advertisements or paid placements should be marked up with rel-sponsored value.
Targets guests: links of guests should be marked up with rel-”nofollow” value.
6. Page Experience Update For Mobile:
Is to make the user experience of the mobile users better. The mobile ranking is affected by the following factors
Largest connect paint (LCP): the time taken for the main content page to appear
First input delay (FID): the response site or page takes to respond to the user
Cumulative layout shift (CLS): the measure of layout movements during the loading of the page.
The following steps will be taken by Google for this algorithm change
- Include a report on Page Experience in the Search Console.
- Eliminate the AMP requirement for Google Search’s Top Stories carousel.
- Take down the AMP badge image.
- Allow signed exchanges (SXG) while searching on Google



